目录
InfluxDB学习笔记
notice: 学习笔记针对的版本是1.7
时序数据库的特点: 持续写入数据量大,数据和时间相关。读取操作相对较少,且通常读取的是一段时间范围内的数据。
存储
LSMTree
组件
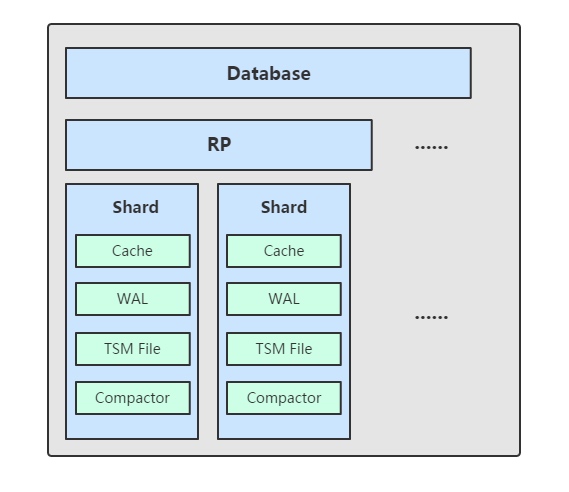
目录结构
|-- data
| |-- NOAA_water_database
| | |-- autogen
| | |-- 3
| | | |-- 000000001-000000001.tsm
| | | |-- fields.idx
| | | `-- index
| | | |-- 0
| | | | |-- L0-00000001.tsl
| | | | `-- MANIFEST
|-- meta
| `-- meta.db
`-- wal
|-- NOAA_water_database
| `-- autogen
| |-- 27
| | `-- _00025.wal
| |-- 29
| | `-- _00025.wal
| |-- 30
| | `-- _00025.wal
Cache
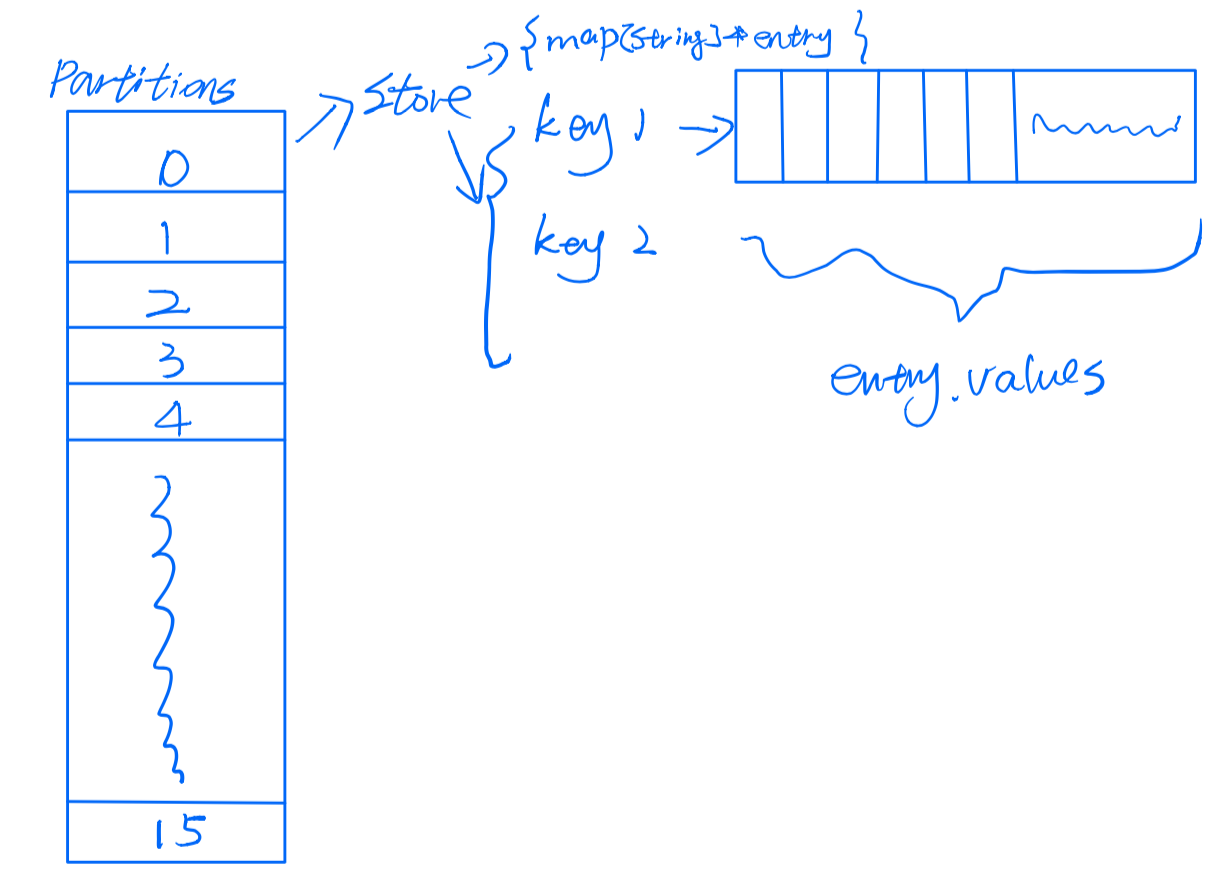
cache存储的设计有点像Java里的ConcurrentHashMap,先根据key hash得到位于哪个分区(partition),在每个分区里,又有独立的map,对于key相同的,value会append到一起,成为一个entry。
//ring.go
type partition struct {
mu sync.RWMutex
store map[string]*entry
}
//cache.go
type entry struct {
mu sync.RWMutex
values Values // All stored values.
vtype byte
}
//ring.go
partitions = make([]*partition, 16)
func (r *ring) write(key []byte, values Values) (bool, error) {
return r.getPartition(key).write(key, values)
}
func (r *ring) getPartition(key []byte) *partition {
return r.partitions[int(xxhash.Sum64(key)%partitions)]
}
func (p *partition) write(key []byte, values Values) (bool, error) {
//...
partition.store[string(key)] = entry
}
//cache.go
func (e *entry) add(values []Value) {
e.values = append(e.values, values...)
}
WAL
wal 文件的内容与内存中的 cache 相同,其作用就是为了持久化数据,当系统崩溃后可以通过 wal 文件恢复还没有写入到 tsm 文件中的数据
在将一条数据写入日志文件里时,会先经过snappy压缩

//wal.go
type WriteWALEntry struct {
Values map[string][]Value
sz int
}
func (l *WAL) WriteMulti(values map[string][]Value) (int, error) {
//...
id, err := l.writeToLog(entry)
//...
}
func (l *WAL) writeToLog(entry WALEntry) (int, error) {
//...
compressed := snappy.Encode(encBuf, b)
if err := l.currentSegmentWriter.Write(entry.Type(), compressed); err != nil {
return -1, fmt.Errorf("error writing WAL entry: %v", err)
}
}
TSM

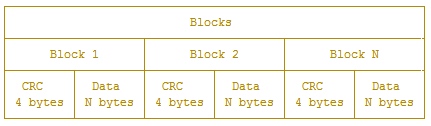
block是InfluxDB中的最小读取对象。 Data中的内容根据数据类型不同有不同的压缩方式
- int64: double delta, zig-zag
- float: double delta, Facebook’s Gorilla, go-tsz
- string: Snappy
- timestamp: run length, simple8b
Index

索引条目的顺序是先按照key的字典序排序,再按照time排序
IndirectIndex
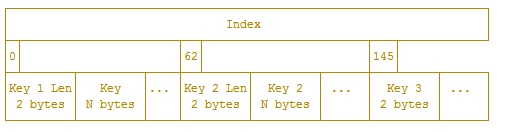

间接索引只存在于内存中,offsets是一个数组,其中存储的值为每一个key在Index表中的位置。 可以通过二分查找,定位到某个key在Index表中的位置,再根据时间定位。
查询与写入
查询(query)
会使用到布隆过滤器(Bloom filter)
写入(write)
数据写入tsm文件的代码
cache写入到tsm文件的触发条件为,cache的大小大于阈值(CacheFlushMemorySizeThreshold)或距cache最后一次写入的时间大于阈值(CacheFlushWriteColdDuration)
去重
//tsm1/engine.go
func (e *Engine) ShouldCompactCache(t time.Time) bool {
sz := e.Cache.Size()
if sz == 0 {
return false
}
if sz > e.CacheFlushMemorySizeThreshold {
return true
}
return t.Sub(e.Cache.LastWriteTime()) > e.CacheFlushWriteColdDuration
}
性能优化
- 考虑时间精度,精度越小,需要更多的存储空间,写入更慢